What’s Testing as a Service? TaaS Explained


Software testing is becoming ever more important, especially in DevOps organizations. That’s due to many reasons:
These drivers extend to the realm of software testing, an integral part of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) process, through mechanisms of continuous testing and automated testing. In this regard, the industry is embracing IT as a utility, where IT operations and testing processes are automated, streamlined, and integrated into modern SDLC frameworks.
 The concept of Software Testing as a Service (TaaS) fits nicely in this domain. Testing as a service is rising in popularity among IT-driven organizations that lack the technology, human, and financial resources necessary for rapid, continuous, and automated testing.
The concept of Software Testing as a Service (TaaS) fits nicely in this domain. Testing as a service is rising in popularity among IT-driven organizations that lack the technology, human, and financial resources necessary for rapid, continuous, and automated testing.
In this article, we will discuss what Testing as a Service means and the capabilities suitable for your IT organization.
Testing as a Service is the outsourcing of activities and operations associated with software testing activities. Like its cloud-based, as-a-service predecessors, the TaaS capabilities are accessed across a Web interface and include several self-service capabilities such as:
TaaS can take various shapes and forms. A complete testing cycle may include end-to-end support and technology capabilities used in planning and conducting software testing. In this mode, you engage a third-party vendor for two main reasons:
In other cases, a TaaS service may be a technology platform that combines the software and hardware components to deliver specific testing capabilities as a service.
The service can be grouped into functional and non-functional aspects of software testing.
Functional testing finds the answer to the simple question:
Does the software behave as expected against a given set of test cases?
Functional testing involves the technology process itself, such as:
Non-functional testing deals with the related aspects of software quality. These include usability, security and performance, among others. Non-functional testing evaluates the behavior of software components in the greater scheme of things:
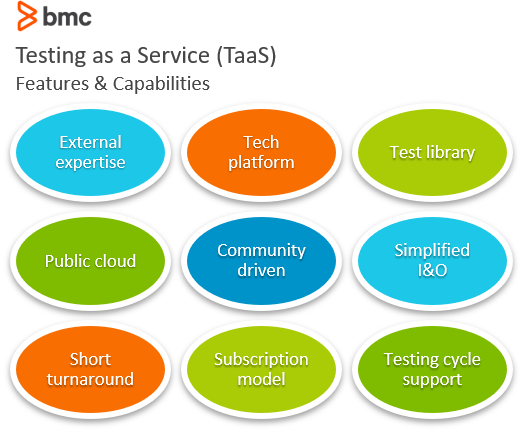
Both functional and non-functional testing is achieved with the following features and capabilities of any good Testing as a Service solution:
Although software quality assurance is integral to the process of building innovative new technologies, the testing process itself isn’t keeping pace with release cycles. According to a recent research survey of tech companies in the North America region by Capgemini, 74% of the respondents suggested that QA was essential for business growth and end-user satisfaction.
However, the current testing practices still lag behind in presenting the desired outcomes. According to the survey, only 29% of the respondents suggested that their testing efforts produce the desired outcomes. The void is primarily associated with the lack of technology resources and expertise available in-house:
With Testing as a Service solutions and automated testing in the cloud, this gap can be filled to validate software quality at the fast pace of DevOps and Agile release cycles.