In this blog post we will introduce a tool developed by Netflix called Spinnaker. We will discuss what it is, overview of its key components and use case. At the end of this post, you should have a good understanding of what Spinnaker is all about.
Continuous delivery and deployment
To understand what spinnaker is used for, it is worth going over two concepts: Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment. Continuous Delivery is a practice by which a software can be deployed to production in a fast, safe and automated manner. The idea here is that new functionality can be built and if all things check out, it can be deployed to production. This is a manual approval to prod.
Continuous Deployment takes this farther. It automatically pushes any change to production as long as it passes any test defined.
Notice how Continuous Delivery can and Continuous Deployment will deploy. As you can see, both of these processes heavily depends on automation and repeatable process for fast release and higher frequency.
What is Spinnaker?
Spinnaker is a tool used for Application Management and Application Deployment, targeted towards cloud services.
- For application management, Spinnaker uses concepts like “Applications”, “Clusters” and “Server Groups” to describe and group deployed services. These services are exposed to users with “Load balancers” and “Firewalls”.
- The application deployment part of spinnaker is made up of three key concepts “Pipelines”, “Stages” and “Deployment Strategies” (red/black, canary). There are a bunch of stages that make up a pipeline and you can set a deployment strategy for the pipeline.
Spinnaker can be used for both continuous delivery and continuous deployment. It is important to note, however, that Spinnaker is not a build tool nor a continuous integration tool like Jenkins. Instead, you can integrate Jenkins with Spinnaker for a full CI/CD stack.
Spinnaker Components
Spinnaker is made up of 11 microservices working together to give us the features that we get out of the box. Let’s go over each service.
- Deck. This is the frontend service for spinnaker. Anytime you are interacting the UI, this service is doing all this work.
- Gate. This is the API gateway that fronts all the other services. Like any other microservice architecture, all communications from the UI or API callers to spinnaker goes through this service.
- Orca. This service is responsible for all ad-hoc operations. Things like taking a pipeline or task definition and managing the stages and tasks. This service is also responsible for persisting information about pipeline execution allowing one stage to get info about another stage. Redis is used to persist this information.
- CloudDriver. This service is responsible for making calls to cloud providers and caching all deployed resources. It is the main integration to all cloud providers.
- Front50. This service is responsible for persisting the metadata of applications, pipelines, projects and notifications.
- Rosco. This service is responsible for baking images that will be deployed. It uses the packer tool to do the baking.
- Igor. This service is used to connect to continuous integration platforms like Jenkins or Travis CI to spinnaker. It also allows Jenkins/Travis CI to be present in the pipeline. Without this service you will not be able to integrate with any CI tool.
- Echo. This service is the event bus responsible for sending notification and responsible for all incoming webhooks to Spinnaker.
- Fiat. This service is responsible for authorization. It is used to query for users permission.
- Kayenta. This service is responsible for automated canary analysis for spinnaker. This is the latest service added to spinnaker so earlier versions of spinnaker did not have this service.
- Halyard. This service is the tool for installing, configuring, and updating spinnaker.
Spinnaker use case
A simple use case is building a pipeline that grabs an artifact from a Jenkins build job, bake an AMI from that artifact, run some test, then deploy to AWS EC2 instance or deploy to a Kubernetes cluster. We can even throw in a manual approval stage before the deployment stage in case we want to notify a group of devs to approve the deployment. This is just a simplified pipeline to help understand the flow.
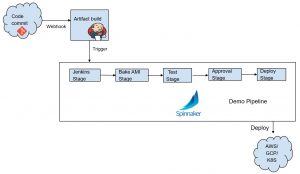 Spinnaker, in this case, will be triggered to run a pipeline after a successful Jenkins build. You can also have spinnaker go trigger a Jenkins build job, then wait for that job to complete before moving on in the stages. It can also simply just grab the artifact from the last build in Jenkins. There are other stages like slacking a dev team that there is an approval waiting, kicking off another pipeline run in a stage or sending off a webhook, just to name a few.
Spinnaker, in this case, will be triggered to run a pipeline after a successful Jenkins build. You can also have spinnaker go trigger a Jenkins build job, then wait for that job to complete before moving on in the stages. It can also simply just grab the artifact from the last build in Jenkins. There are other stages like slacking a dev team that there is an approval waiting, kicking off another pipeline run in a stage or sending off a webhook, just to name a few.
Installing Spinnaker
Installing spinnaker can be done two ways:
- You can install a production ready cluster with the Halyard service and you can find instructions here.
- You can also just build each microservice from source from here. Building each service from source mean you will have more configuration to setup and you will have to understand how the services interact. As you can see, it requires a lot more work.
Spinnaker is a powerful tool that can help streamline application deployment in an automated repeatable fashion with the ability to build best practice into the pipeline. For more on this topic, see Using Spinnaker with Kubernetes for Continuous Delivery.


 Spinnaker, in this case, will be triggered to run a pipeline after a successful Jenkins build. You can also have spinnaker go trigger a Jenkins build job, then wait for that job to complete before moving on in the stages. It can also simply just grab the artifact from the last build in Jenkins. There are other stages like slacking a dev team that there is an approval waiting, kicking off another pipeline run in a stage or sending off a webhook, just to name a few.
Spinnaker, in this case, will be triggered to run a pipeline after a successful Jenkins build. You can also have spinnaker go trigger a Jenkins build job, then wait for that job to complete before moving on in the stages. It can also simply just grab the artifact from the last build in Jenkins. There are other stages like slacking a dev team that there is an approval waiting, kicking off another pipeline run in a stage or sending off a webhook, just to name a few.