What Is Data Architecture? Components, Principles & Examples


Data architecture is a framework for how IT infrastructure supports your data strategy. The goal of any data architecture is to show the company’s infrastructure, including how data is acquired, transported, stored, queried, and secured.
Data architecture is the foundation of any data strategy.
AI technology is radically changing data infrastructures, specifically data architecture and strategies for handling data. Data architecture defines how your organization captures data, how it’s stored and managed, and how that data is used. AI applications demand better ways to handle massive volumes of data, as well as increases in computational capacity.
To handle sophisticated AI applications, your data infrastructure must support agility, both for rapidly changing business demands and to handle the fast pace of AI innovation. Your data architecture has to be highly efficient, resilient, and strong, and it must also offer scalability.
How can you achieve these requirements?
In this article, we’ll look at:
Let’s get started.
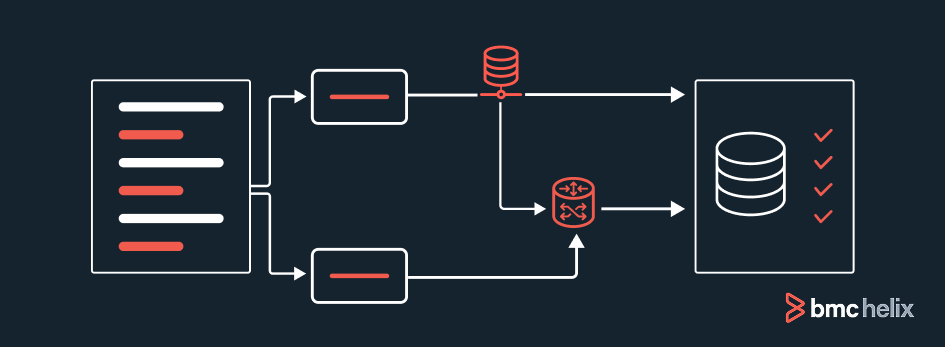 Data architecture is the structure and organization of how you acquire data, store it, and manage it, and ultimately how your systems access and use it. Data architecture components include data models, rules and policies, data access and security technologies, and analytical processes and outputs.
Data architecture is the structure and organization of how you acquire data, store it, and manage it, and ultimately how your systems access and use it. Data architecture components include data models, rules and policies, data access and security technologies, and analytical processes and outputs.
Data architecture resolves the “how” for implementing your data strategy.
Different data architecture examples include:
The data architecture is 100% responsible for increasing a company’s freedom to move around the world.
If agility is what is needed to avoid collapse during slow seasons or to capitalize on the spontaneous popularity of a new product, the more advanced the data architecture is, the more capable the company is to take action.
Explicitly, data architecture is important because it:
The architectural components of today’s data architecture world are:
A data architecture framework is a structured approach to defining your data strategy, including how to organize data, process it, analyze it, and document it.
Data standards are the overarching standards of a data architecture, which you apply to areas such as data schemas and security.
A data schema defines how you organize data within a database, including specifying its format, relationships, and standards for storage and access. The data schema spells out:
Most companies update their data schema around changing business needs, applications, and data models. As data becomes increasingly pervasive, companies are shifting away from on-premise databases to scalable cloud-native relational databases.
You can easily add data and combine data from a network of data sources into today’s relational (NoSQL) databases without being restricted to a fixed hierarchy. Plus, these relational databases can grow much larger and handle adding data dynamically through integrations with analytics tools that are not possible with traditional SQL databases.
Updating and modifying your data schema, or “versioning” it, is vital. Versioning the data schema helps standardize what to find, where, and the ability to ask when a data set was in a location.
(Explore data storage from database to warehouse to lake and from hot to cold.)
Data standards also help set the security rules for the architecture. These can be visualized in the architecture and schema by showing what data gets passed where, and, when it travels from point A to point B, how the data is secured.
Security protocols can include:
AI is driving data architecture trends, reflecting the need for processing data in real time, handling massive volumes of data from diverse sources in a multiplicity of formats, and supporting highly sophisticated queries and analytics. Trends include:
When thinking about anything related to data — which is arguably everything — you should always consider the data architecture.