Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI): An Introduction


Companies can use process quality frameworks like the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)to standardize workflows, reduce errors, and ultimately improve efficiency. By optimizing the way you operate, you can achieve high-quality and predictable outcomes that give you a competitive edge.
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a framework for optimizing processes to produce high-quality outcomes efficiently. It is a structured approach to assessing process definition and how well they are managed and continuously improved.
While CMMI was originally tailored towards software engineering, the latest version is much less specific. Today, you can apply CMMI to hardware, software, and service development across all industries. The model enables organizations to measure, build, and improve capabilities—to improve overall performance.
Let's take a look at CMMI.
According to the CMMI Institute, a primary goal of CMMI is creating “reliable environments where products, services and departments are proactive, efficient and productive.”
More specifically, CMMI’s objectives for businesses include enabling your organization to:
According to the Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute, which was integral in its development, CMMI is intended to:
Help “integrate traditionally separate organizational functions, set process improvement goals and priorities, provide guidance for quality processes, and provide a point of reference for appraising current processes.”
CMMI was developed by Carnegie Mellon University as part of the CMMI project. Its goal was to make maturity models—which measure the ability of organizations to have ongoing improvement in a particular area—more effective and usable by integrating a number of models into a single framework.
(Learn about digital maturity models.)
The project, whose main sponsors were the Office of the Secretary of Defense and the National Defense Industrial Association, included members of industry, government, and the Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute (SEI). Models were initially created for the Department of Defense to assess the expertise and quality of software contractors.
The first version of the CMMI was released in 2002 and built upon the Capability Maturity Model (CMM), which was developed from 1987 to 1997. In 2002, version 1.1 was released, in 2006 version 1.2 was released, and in 2010 version 1.3 was released. Version 2.0 launched in 2018 with some notable changes that make the model more accessible and effective for businesses in any industry.
The CMMI is administered by the CMMI Institute, which was bought by ISACA in 2016. (Today known only by its acronym, ISACA was formerly known as the Information Systems Audit and Control Association. ISACA also owns the COBIT framework and a variety of certifications.)
The stated goal of the CMMI Institute is to
“Enable[] organizations to elevate and benchmark performance across a wide range of critical business capabilities, including product development, service excellence, workforce management, data management, supplier management, and cybersecurity.”
Organizations that want to better understand how their practices compare to CMMI best practices and want to implement CMMI practices often start with an appraisal. Generally, a business decides to be appraised for one or more reasons, including to:
The CMMI appraisal process primarily evaluates three areas:
While going through the appraisal process can be time-consuming and expensive for organizations, doing so provides some distinct benefits. Benefits of appraisals include:
Any appraisals using the CMMI model must comply with the requirements in the Appraisal Requirements for CMMI (ARC) document. The official appraisal method used by the CMMI Institute is known as the Standard CMMI Appraisal Method for Process Improvement (SCAMPI). Within this approved method, there are three classes of appraisal methods.
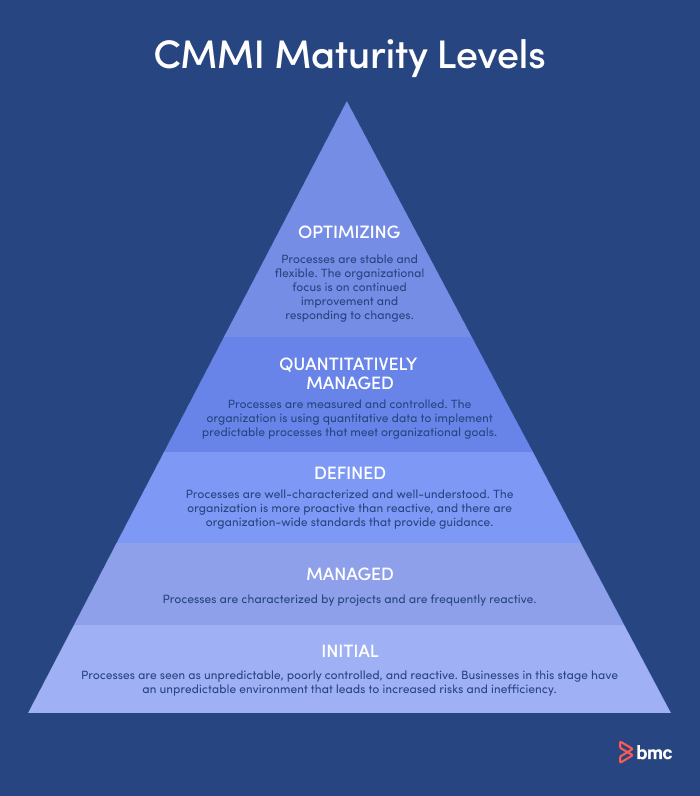
When a Class A appraisal is done, an organization is awarded either a maturity level rating or a capability level rating. Maturity level ratings range from 1 to 5, with level 5 being the highest level and the goal towards which organizations are working.
It’s worth noting that while the goal of organizations is to reach CMMI level 5, the model is still applicable and beneficial for organizations that have achieved this maturity level. Organizations at this level are primarily focused on maintenance and improvements, and they also have the flexibility to focus on innovation and to respond to industry changes.
Over time, CMMI has changed primarily in an effort to make models easier for businesses to understand and implement. Additionally, the changes aim to make CMMI more cost-effective for businesses to integrate and use. The newest version, CMMI V2.0 was released in 2018. According to the CMMI Institute, this version was created with the goals of:
Further, the CMMI institute asserts that version 2.0 will improve customer satisfaction, lead to increased customer acquisition and retention as well as increased productivity and efficiency, and reduce the risks associated with CMMI.
CMMI V2.0 has five components that are intended to work together to provide businesses with a clear path to achieve their objectives. The five components are:
This model is intended to make it easier than ever for businesses to utilize CMMI to improve their overall performance. To learn more about CMMI and about how your business can benefit from this model, visit the CMMI Institute.