AWS ECS vs AWS Lambda: What’s The Difference & How To Choose


There are several options for code and application deployment in the AWS ecosystem. Two of the most popular options for AWS application deployment are:
Today, let’s look at ECS and Lambda, explaining what each option does and discuss some critical considerations for deploying one option over another.
(This article is part of our AWS Guide. Use the right-hand menu to navigate.)

ECS is used to manage and deploy Docker containers at scale (container orchestration).
ECS uses the following AWS components to store and run ECS applications:
Let’s take a look.
ECR manages, stores, compresses, secures, and controls access to container images. Alternatively, you can use Docker Hub for storing and accessing container images.
A cluster is a logical grouping of tasks and containers that use several different launch types (infrastructure) to run. Clusters can contain:
When adding EC2 instances to an ECS cluster, you will need to manage the EC2 servers in that cluster, including locking down EC2 security, access, patching their operating systems, and performing maintenance.
AWS Fargate is a serverless computing environment that works with ECS. When adding Fargate tasks to an ECS cluster, AWS provisions and manages the EC2 servers your containers run in, relieving you from administering a separate EC2 infrastructure.
Amazon ECS Anywhere is an ECS extension that allows you to run containerized applications on servers outside the AWS ecosystem. ECS Anywhere loads an agent onto customer managed operating systems, making them managed instances and allowing those instances to register into an ECS cluster.
Task definitions that describe 1-10 containers (and parameters) that define an ECS application. Task definitions are stored as JSON files.
This service schedules tasks (instantiations of the task definitions) to run inside your ECS cluster infrastructure. It executes tasks on a cron-like schedule or your own custom schedule.
The task scheduler also:
AWS is also integrated with other AWS services.
Putting it together, the ECS service scheduler launches tasks into ECS clusters using task definitions that reference and use Docker containers stored in the Elastic Container Repository or Docker Hub.
Using ECS is notable in that you can define your own EC2 server cluster, let AWS manage and deploy EC2 servers (AWS Fargate), use external servers (ECS Anywhere), or a combination of the three. Clusters and ECS tasks run inside specified AWS Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and subnets.
AWS Lambda excels at running smaller on-demand applications that are triggered by new events and information.
Lambda is an AWS service that runs code without the need to provision and manage infrastructure. There is no EC2 provisioning or clusters to define. Lambda totally controls the EC2 instances your code runs on, and it auto-scales as needed. Lambda operates at the function and code level in the following way:
Lambda supports many languages through Lambda runtimes, including nodeJS, Python, Go, Java, Ruby, .Net, and C#.
Package your code in a zip or jar deployment package, and upload it using the Lambda console or AWS CLI.
You designate the file and function name that serves as your entry point. Once uploaded, Lambda provides an Amazon Resource Name (ARN), which serves as an ID for the function you just created.
Your Lambda function is invoked and runs on EC2 instances
Lambda functions can be invoked several ways, including:
Functions can be invoked either:
After the function’s initial call, Lambda can scale by an additional 500 instances per minute when traffic spikes, until there are enough instances to handle the traffic. Scaling continues until a Lambda concurrency limit is reached or requests come in faster than your function can scale. You can also contract for provisioned concurrency to prevent Lambda scaling waits. As traffic dies down, Lambda stops unused instances.
Lambda provisions serverless application deployment, including:
Your main responsibility is setting up your functions and invocation configurations. Lambda does the rest. Lambda functions are easy to set up and worry-free as far as infrastructure goes.
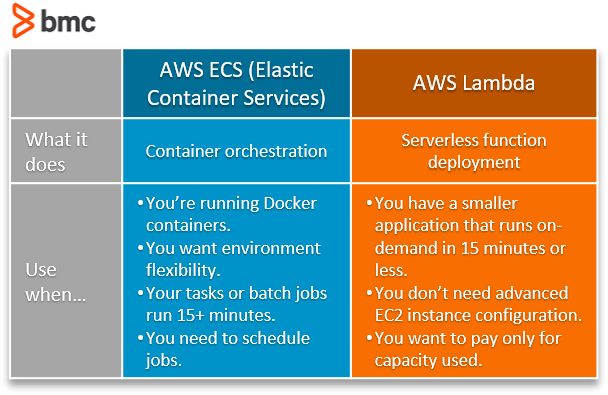
Now that we’ve looked at what each application deployment option does and how it works, here are some considerations in choosing one option over the other.
Generally, ECS is best used for running a Docker environment on AWS using clustered instances. Lambda is best used for quickly deploying small, on-demand applications in a serverless environment.