AWS Certifications in 2022


Amazon Web Services (AWS) certifications are highly sought-after credentials in today’s environment. AWS certs provide an industry standard for demonstrating AWS cloud expertise, rigorously testing competency, and providing an accurate representation of the test-taker’s skills.
This article covers several aspects of getting and maintaining an AWS certification. We’ll look at the following topics and how they relate to your AWS certification journey:
(This article is part of our AWS Guide. Use the right-hand menu to navigate.)
There are eleven active AWS certifications that you can achieve in 2022:
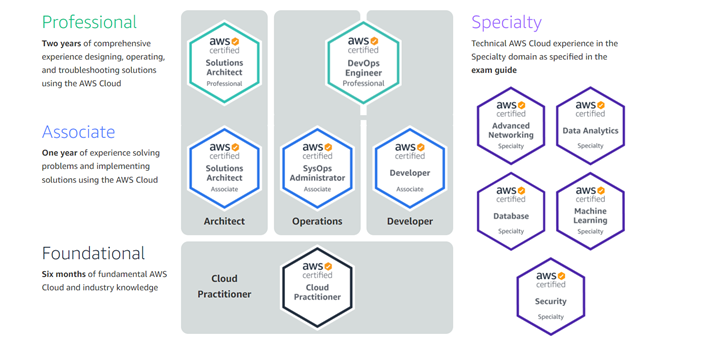
(Source)
Here’s a brief description of what each certification level offers and what proficiencies they certify.
Cloud Practitioner is the only Foundational AWS certificate. It is ideal for candidates with at least six months of experience in any role involving the AWS cloud, such as technical, sales, purchasing, financial, or managerial positions.
This certification verifies that the candidate has an overall familiarity with the AWS Cloud and related knowledge and skills. While other certifications tie into specific technical roles such as Architect, Developer or Operations, the Cloud Practitioner certification provides a more general foundation for any career path.
Each of the Associate certifications typically require at least a year of previous direct experience and knowledge regarding AWS services and related technologies. The three certifications within the Associate level are:
The highest certification category, each Professional AWS certification requires a full two years of experience, with each candidate being successful and highly capable within their respective roles. The two Professional-level certifications are:
Whereas the previous three levels represent the core role-based certifications that AWS offers, the Specialty certifications provide evaluations in specific technical areas. These certifications include:
Requirements vary for each specialty certification. Candidates must possess experience with AWS technology, along with 2-5 years’ experience in the specialty domain. Check each individual certification for prerequisites and requirements.
To earn an AWS certification, you’ll have to pass a test. Each exam requires an AWS testing fee, typically between $100 and $300 (visit this page for Amazon’s current pricing).
Be prepared though—the examination fee won’t be your only certification cost. You may also have to invest cash and time in test preparation, including:
But there is an upside! Amazon offers an AWS Free Tier account for trials, 12 months free access, and some free-tier services that you never need to pay for. This is valuable when studying for certification. However, if you’re studying specific certification scenarios, you may have to purchase additional services with your free account.
AWS remains one of the top cloud service providers in the market. For good reason.
Obtaining AWS certifications demonstrates competency in AWS services. They also help candidates clearly demonstrate to potential employers exactly what skills they have, which helps you to:
Many significant IT professional and management opportunities aren’t available without a related AWS certification. While great salaries aren’t guaranteed, AWS certified jobs frequently can offer salaries ranging from $90k to $160k+ USD, depending on the AWS certification category and job environment.
Of course, AWS certifications can also aid candidates in improving skills or learning new ones. Preparing for the exams through practice exercises and studying can:
The two main factors that determine appropriate AWS certification needs are the experience level and career path desires of the candidate. If you already work in a particular field and wish to move up to higher positions, look for certifications that match your capabilities. Then, check the requirements in terms of experience and skills to determine if an Associate, Professional, or Specialty certification is the best fit.
AWS outlines several “learning paths” that can help guide candidates toward the best certifications for obtaining specific professional roles in the future.
If you’re just starting out, the Foundational Cloud Practitioner certificate can be a good choice. Explore the various learning paths to help identify specific professional goals and the best certificates to reach them.
There are many options for exam preparation. Useful ways to get ready for AWS certification include:
Training classes are available through AWS, and third-party global and local AWS training partners. You can find AWS approved instruction at the AWS Classroom Training Overview web page.
Remote and (sometimes) in-person training offer the best options for learning AWS skills and certifications. They provide instructor-led training and labs, as well as practice exams, books, and exercises. Amazon also offers study guides in both ebook and physical formats.
Studying for any given exam is likely to require anywhere from 80 to 120 hours.
For candidates working full-time jobs, this can mean months of preparation. Start a study regimen about two or three months before the exam date with a consistent weekly schedule designed to cover all the relevant material in the given timeframe. Certification exams cover a lot of material in an Amazon-specific format so give yourself plenty of time to absorb the material.
Regarding exam practice, regularly take the certification practice tests provided with your study materials. Even if you’ve been working with the material for years, certification exam questions may contain specific terminology and phrasings that you’re unfamiliar with. Taking the practice tests help prepare you for the tone and pace of the exam.
For more details on the format, type, delivery method, time limit, costs, and available languages of each exam, check the page of your intended certification by clicking on its badge on the AWS learn about training by role or solution page.